There may be situations when you need to repeat your code / Looping. In SAP ABAP, statements are executed sequentially: The first statement in a function is executed first, followed by the second, and so on. Loop statements allow us to execute a statement or group of statements several times and the following is the general form of a loop statement in most programming languages.
The ABAP programming language provides 3 types of Loop statements such as:
- WHILE loop
- Do loop
- Nested loop
WHILE loop
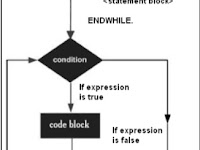
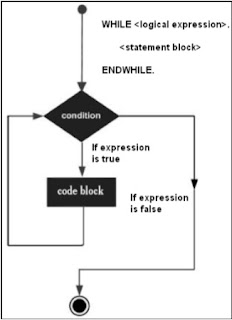
WHILE loop statements repeatedly execute target statements as long as certain conditions are true.The general format of the WHILE command is as follows:
WHILE
.
ENDWHILE.
A block statement can be a single statement or a block statement. While Loop executes the statements attached by the WHILE and ENDWHILE commands until the logical expression becomes false.Example:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
|
REPORT YS_SEP_15.
DATA: a type i.
a = 0.
WHILE a <> 8.
Write: / 'This is the line:', a.
a = a + 1.
|
The output is
This is the line: 0
This is the line: 1
This is the line: 2
This is the line: 3
This is the line: 4
This is the line: 5
This is the line: 6
This is the line: 7
Do loop
The unconditional loop repeatedly makes several statements without specifying any conditions. The DO statement applies the unconditional loop by executing a set of statement blocks several times without conditions.Syntax'Times' imposes restrictions on the number of loop paths, represented by 'n'. The value 'n' cannot be negative or zero. If zero or negative, the statement in the loop cannot be executed
Example:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
|
Report YH_SEP_15.
Do 15 TIMES.
Write: / 'Hello'.
ENDDO.
|
The output is:
Hello
Hello
Hello
Hello
Hello
Hello
Hello
Hello
Hello
Hello
Hello
Hello
Hello
Hello
Hello
Nested loop
DO and WHILE statements can be tested and combined with other forms of loops. Each nested loop will have its own SY-INDEX which is created and monitored by the system.
DO [n TIMES].
.
DO [m TIMES].
.
ENDDO.
ENDDO.
Example:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
|
REPORT YS_SEP_15.
Data: a1 type I, b1 type I.
a1 = 0.
b1 = 0.
Do 2 times.
a1 = a1 + 1.
Write: /'Outer', a1.
Do 10 times.
b1 = b1 + 1.
Write: /'Inner', b1.
ENDDo.
ENDDo
|
The output is:
Outer 1
Inner 1
Inner 2
Inner 3
Inner 4
Inner 5
Inner 6
Inner 7
Inner 8
Inner 9
Inner 10
Outer 2
Inner 11
Inner 12
Inner 13
Inner 14
Inner 15
Inner 16
Inner 17
Inner 18
Inner 19
Inner 20
In this example, the outer DO loop is processed twice and the inner DO loop is processed 10 times, each time the outer DO loop is processed. So in this case, the inner loop is processed 20 times.